Honeypots: Turning the Tables on Hackers
In the cat-and-mouse game of cybersecurity, defenders are constantly seeking innovative ways to outmaneuver malicious actors. One such ingenious tool in the cybersecurity arsenal is the honeypot—a deceptive trap designed to lure hackers into revealing their tactics, techniques, and intentions. While the concept of a honeypot might sound like something out of a spy thriller, its real-world applications are both fascinating and crucial in the ongoing battle against cyber threats.
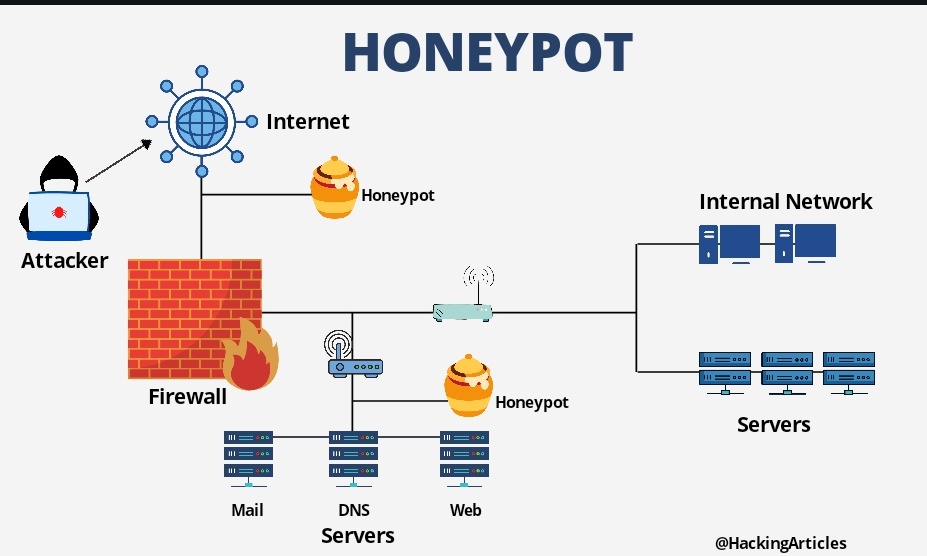
Unveiling the Honeypot
Imagine a virtual trap, meticulously crafted to mimic a legitimate system or network component. This could be a fake server, a dummy database, or even an entire network segment designed to attract the attention of cybercriminals. The allure lies in the seeming vulnerability of the honeypot, enticing hackers to exploit it.
How Honeypots Work
Honeypots are intentionally designed with vulnerabilities or enticing data that would attract an attacker. They are placed strategically within a network or system, often in locations where real assets are located. Once a hacker takes the bait and interacts with the honeypot, its purpose is twofold:
- Gathering Threat Intelligence: Every action taken by the attacker within the honeypot is meticulously logged and analyzed. This includes attempted exploits, malware samples, command inputs, and even lateral movement within the decoy environment. By observing these activities, cybersecurity professionals gain valuable insights into the tools and tactics used by hackers.
- Diverting Attention: Honeypots serve as a distraction, diverting the attention of attackers away from critical assets. While hackers are occupied with the decoy system, defenders have the opportunity to fortify real systems, update defenses, and prepare countermeasures.
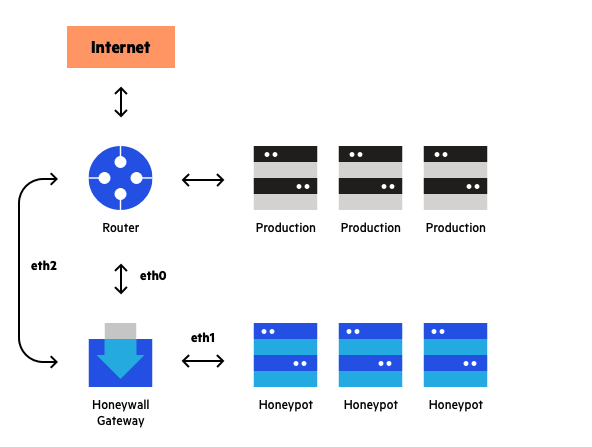
Types of Honeypots
Honeypots come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
- Research Honeypots: These are designed primarily for gathering threat intelligence. They are often low-interaction, meaning they simulate only basic services to observe attacker behavior without risking the compromise of critical systems.
- Production Honeypots: Unlike research honeypots, production honeypots are deployed within a live environment alongside real assets. They closely mimic the behavior and vulnerabilities of legitimate systems, serving both as a diversion and as a means to detect and block attacks in real-time.
- High-Interaction Honeypots: These are fully-featured emulations of entire systems or networks. They allow attackers to interact deeply with the environment, providing a wealth of information to defenders. However, they also carry a higher risk, as sophisticated attackers might detect their true nature.
Advantages of Honeypots
- Early Threat Detection: Honeypots can detect threats at the reconnaissance stage, long before an attacker reaches critical systems.
- Understanding Attack Techniques: By analyzing hacker interactions, cybersecurity professionals gain insights into new and emerging attack methods.
- Enhanced Incident Response: Real-time alerts from honeypots allow for swift incident response, minimizing potential damage.
- Legal and Ethical: Since honeypots are designed as traps, their use falls within legal and ethical boundaries when deployed within one’s own network.
Challenges and Considerations
While honeypots are powerful tools, their deployment requires careful planning and consideration:
- Resource Intensive: Honeypots require dedicated resources for maintenance, monitoring, and analysis.
- False Positives: Interactions with honeypots might sometimes be triggered by legitimate activities, requiring skilled analysts to differentiate between real threats and benign events.
- Deception Maintenance: To remain effective, honeypots must stay updated to mimic current systems accurately.

Conclusion: Turning the Tables
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, defenders are tasked with staying one step ahead of cyber threats. Honeypots offer a proactive and strategic approach, allowing organizations to gain valuable insights into the minds of attackers while bolstering their defenses.
By turning the tables on hackers and enticing them into carefully crafted traps, cybersecurity professionals gather invaluable intelligence, fortify critical systems, and create a formidable line of defense against even the most sophisticated adversaries.
In the intricate dance between defenders and attackers, honeypots stand as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of cybersecurity excellence. As organizations continue to embrace these deceptive tools, the balance of power in the cyber realm shifts, with defenders gaining a crucial edge in the ongoing battle for digital security.






)